Data Analytics for LHC Cryogenics
LHC cryogenics is a complex large-scale system that contains about 60 000 signals. Each day, about 100 millions of datapoints are archived in the CERN databases.
In order to perform efficently some calculations and analysis on this large amount of data, sophistifacted data analytics techniques are mandatory.
Methodology
LHC cryogenics data are archived in the so-called NXCALS database managed by CERN.
Recently, a new platform called SWAN (Service for Web based ANalysis) has been setup at CERN to allow interactive
data analysis using the CERN cloud infrastructure. Different technologies and languages are available for such analysis.
For LHC cryogenics data, we use jupyter notepook in Python language and data are recovered in NXCALS by using the CERN Spark Cluster.
Example: LHC heat load calculations
Input data- All beam screen cryo instrumentation (7x485 loops = 3400 sensors)
- All beam screen parameters (6x485 loops = 2900 parameters)
- For a LHC fill of 15 hours (re-sampled at 1min): about 30 MB of data
Output data
- Beam Screen heat load over time for each cooling loop
- Beam Screen heat load average for each cooling loop during the 15 min after Stable beams
- Beam Screen heat load average for each ARC during the 15 min after Stable Beams
- Beam Screen heat load total for each sector during the 15 min after Stable Beams
- Plots corresponding to these data (see below)
The data retrieval, the resampling and the calculations for a typical LHC fill of about 15 hours takes around 10 minutes.
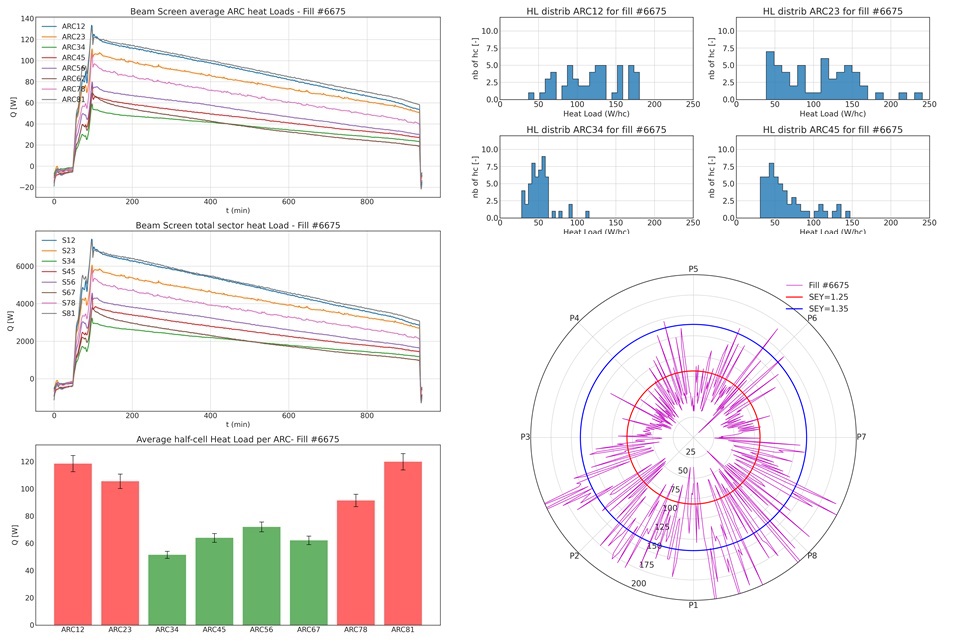
Output generated by the beam screen heat load analysis over one LHC fill
References
- J. Wozniak, C. Roderick. NXCALS - Architecture and challenges of the next CERN accelerator logging service. ICALEPCS 2019.
- D. Pipare et al. SWAN: A service for interactive analysis in the cloud. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018.
- O. Martensson, B. Bradu, G. Ferlin. Signal analysis for automated diagnostic applied to LHC cryogenics. ICALEPCS 2019.
Contact : benjamin dot bradu at cern dot ch
© Copyright Benjamin Bradu's HomePage all rights reserved
Last update: December 2021
© Copyright Benjamin Bradu's HomePage all rights reserved
Last update: December 2021
 HOME
CRYOGENICS
HOME
CRYOGENICS